Basic theory
Completion requirements
If you are new to eArchiving we strongly recommend you start by reading this handbook
https://www.dpconline.org/handbook
Basic principles
Digital preservation refers to the reliable preservation of digital information for several decades or even centuries. Hardware, software, and file formats will become outdated, while the information must be preserved. Reliable digital preservation requires active monitoring of information integrity and anticipation of various risks. Metadata, which describes, for example, the information content, provenance information and how the content can be used, has a key role in this.
- Store and preserve digital information in a cost-efficient manner over the long term.
- Material can be born digital or digitized analog material.
- Usability and equivalency to original must be maintained despite when and with what kind of devices the preserved item will be used.
OAIS Reference model / VS EARK-architecture
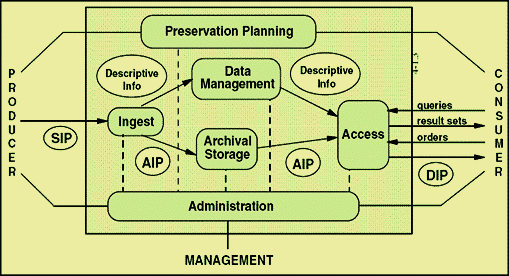
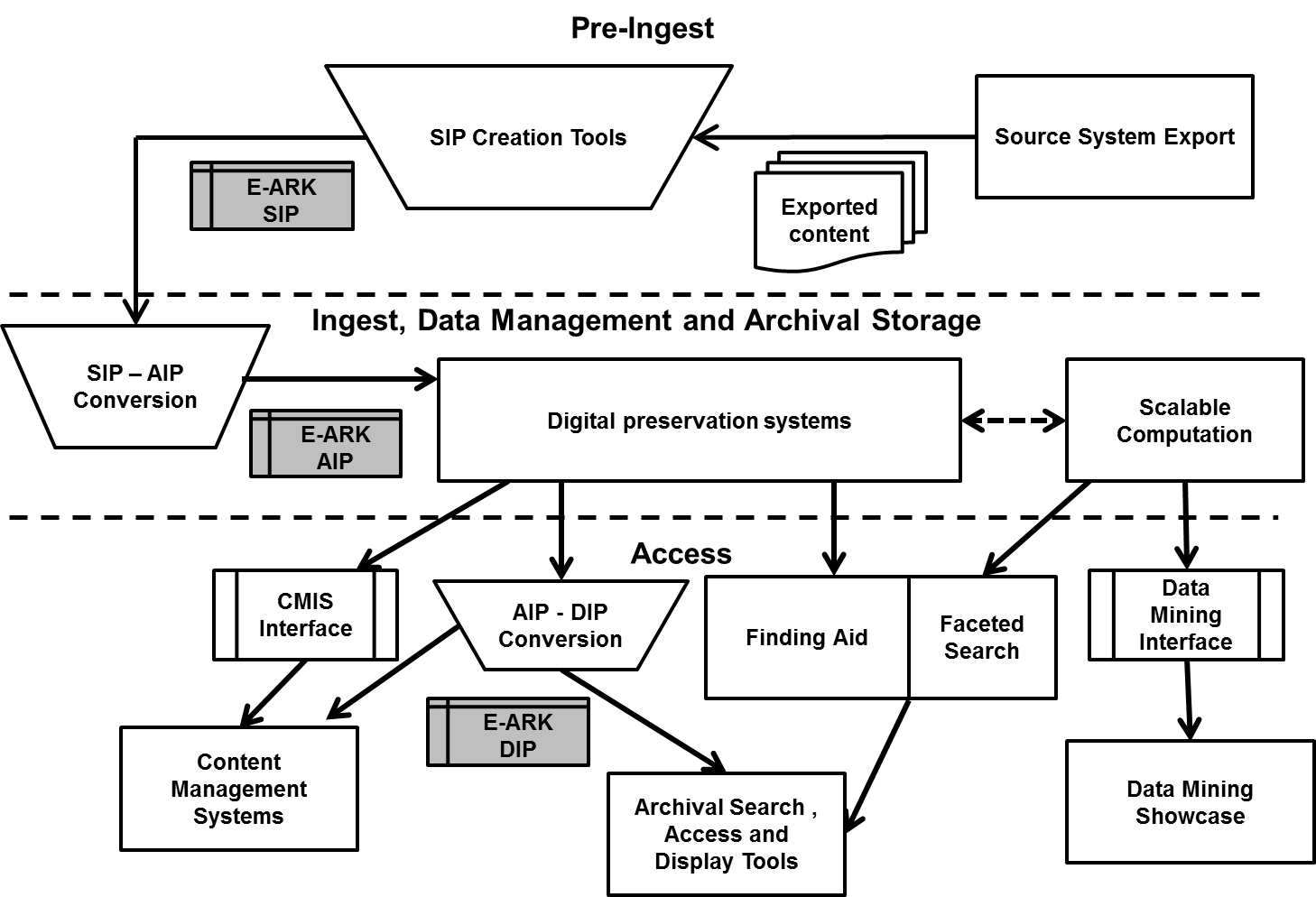
A model that should be followed by every self respecting archival institution
- Producer: The information producer
- SIP: Submission Information Package, a package format that is defined and accepted by archives
- AIP: Archival Information Package, a package created from the received SIP package by archive processes
- DIP: Dissemination Information Package, a package submitted to customers
- EARK archive tools: https://www.eark-project.com/resources/eark-tools
Last modified: Thursday, 18 June 2020, 3:57 PM
